

Cho DW, Kim BS, Jang J, Gao G, Han W, Singh NK. Comparative analysis of two porcine kidney decellularization methods for maintenance of functional vascular architectures. Nano-immunoengineering: opportunities and challenges.
Organ-derived decellularized extracellular matrix: a game changer for bioink manufacturing. Recent development and biomedical applications of decellularized extracellular matrix biomaterials. Yao Q, Zheng YW, Lan QH, Kou L, Xu HL, Zhao YZ. Bioprinting tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink for regeneration and tissue models of cartilage and intervertebral discs. Vernengo AJ, Grad S, Eglin D, Alini M, Li Z. Effect of hierarchical scaffold consisting of aligned dECM nanofibers and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) struts on the orientation and maturation of human muscle progenitor cells. Lee H, Kim W, Lee J, Yoo JJ, Kim GH, Lee SJ. Papers of special note have been highlighted as: dECM has also been processed as scaffolds and drug-delivery vehicles, and utilized for regeneration. A detailed assessment of the dECM provides information on the microarchitecture, presence of ECM proteins, biocompatibility and cell proliferation. A culmination of different methods of decellularization is optimized, which offers a suitable microenvironment mimicking the native in vivo topography for in vitro organ regeneration.

In this review, we focus on the detailed methodology of diverse decellularization techniques for various organs of different animals, and the biomedical applications employing the dECM.
Extracellular matrix free#
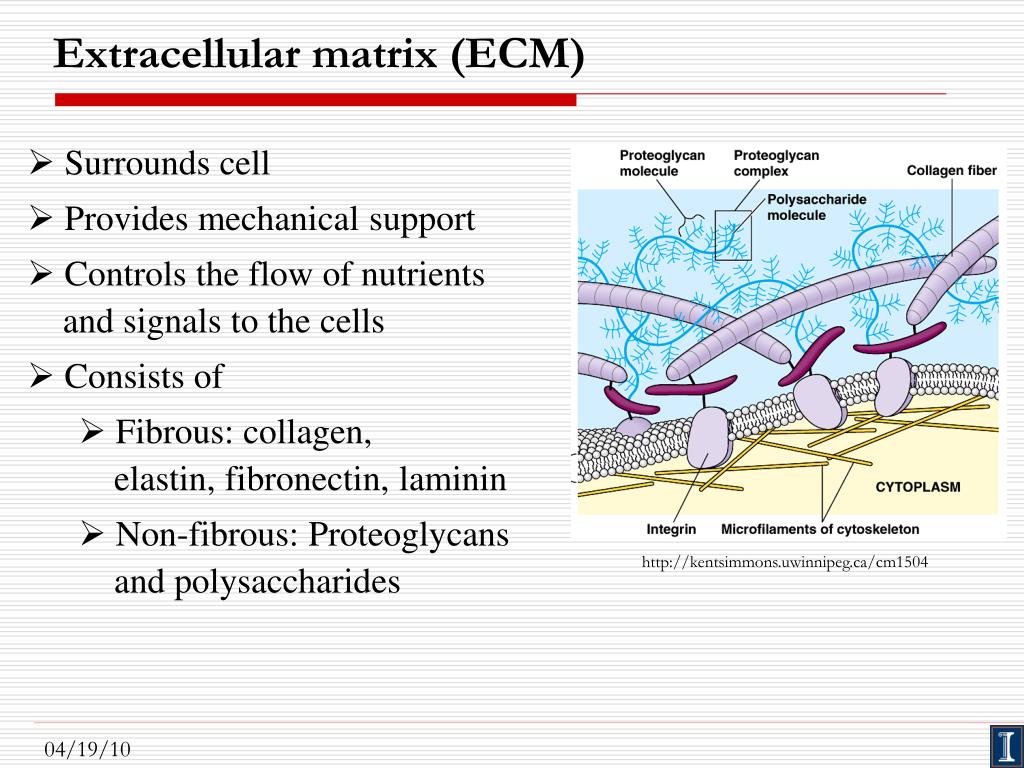
Decellularization technique provides decellularized ECM (dECM), free of cells while preserving the in vivo biomolecules. The extracellular matrix (ECM) forms the integral part of the scaffold to induce cell proliferation thereby leading to new tissue formation. The concept of tissue engineering involves regeneration and repair of damaged tissue and organs using various combinations of cells, growth factors and scaffolds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
